Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a viral infection that affects the nerves and skin. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which is the same virus that causes chickenpox. After a person has chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the nervous system and can reactivate years later, causing shingles. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment options for shingles.
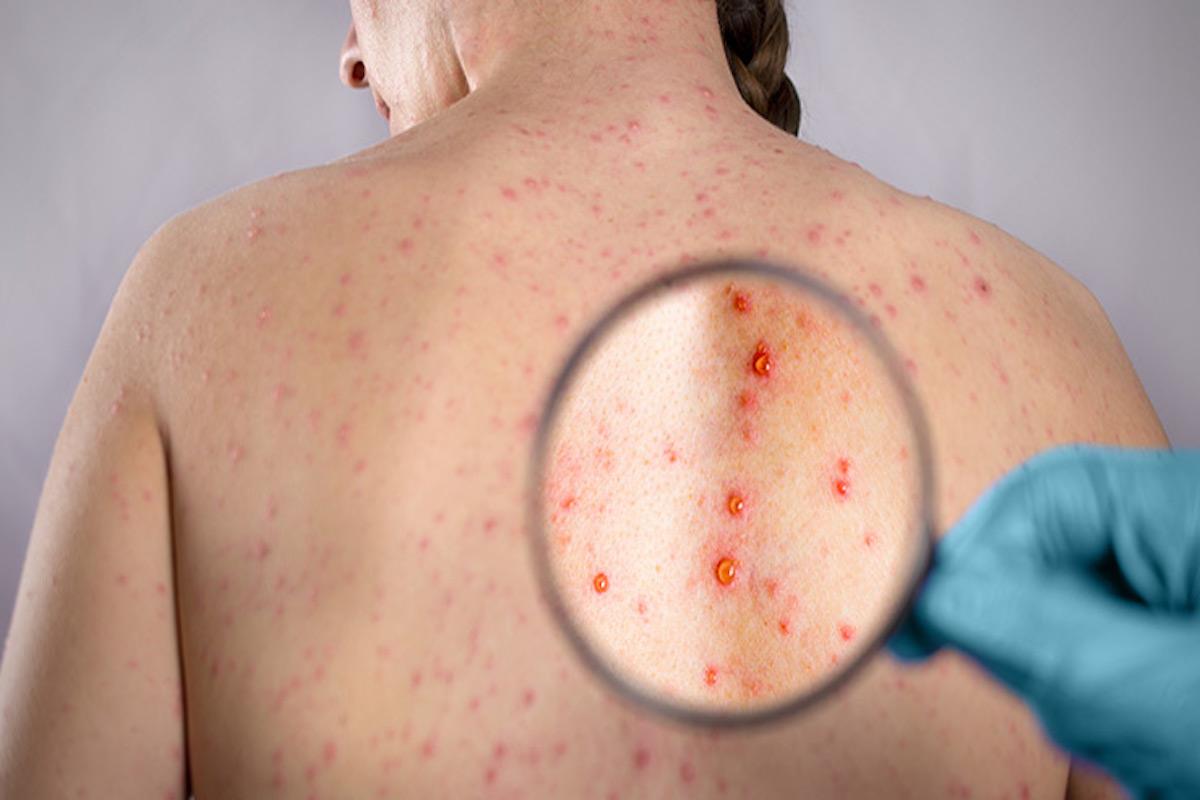
Symptoms of Shingles:
The most common symptom of shingles is a painful rash that typically appears on one side of the body, often in a band or stripe. The rash can be accompanied by itching, burning, and tingling sensations. Other symptoms of shingles may include fever, headache, fatigue, and sensitivity to light. In some cases, shingles can lead to complications such as vision loss, hearing loss, and nerve damage.
Causes of Shingles:
As mentioned earlier, shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which is the same virus that causes chickenpox. After a person has chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the nervous system. When the immune system weakens or is compromised, the virus can reactivate and cause shingles. While the exact reason why the virus reactivates is not fully understood, it is thought that factors such as aging, stress, and a weakened immune system can increase the risk of developing shingles.
Risk Factors for Shingles:
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing shingles. These include age, as shingles is more common in older adults, and a weakened immune system due to factors such as illness, medication, or chemotherapy. Additionally, people who have had chickenpox, especially at a young age, are more likely to develop shingles later in life.
Treatment Options for Shingles:
While there is no cure for shingles, treatment can help manage symptoms and speed up the healing process. Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate pain and reduce fever. Additionally, applying cool compresses or taking cool baths can help relieve itching and burning sensations. In some cases, prescription medications such as antidepressants or anticonvulsants may be prescribed to help manage pain.
Preventing Shingles:
The most effective way to prevent shingles is through vaccination. The shingles vaccine is recommended for adults aged 50 years and older, and is designed to help prevent shingles and its complications. It is a two-dose vaccine, and both doses are necessary for maximum protection.
In addition to vaccination, other preventive measures include maintaining a healthy immune system through a balanced diet, exercise, and stress management, as well as avoiding contact with individuals who have shingles or chickenpox.
In conclusion, shingles is a viral infection that can cause a painful rash and other uncomfortable symptoms. While there is no cure for shingles, treatment options are available to manage symptoms and speed up the healing process. Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent shingles, and maintaining a healthy immune system can also help reduce the risk of developing this condition. If you think you may have shingles, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible to receive a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Looking for pictures of all skin rashes? Find it here:
